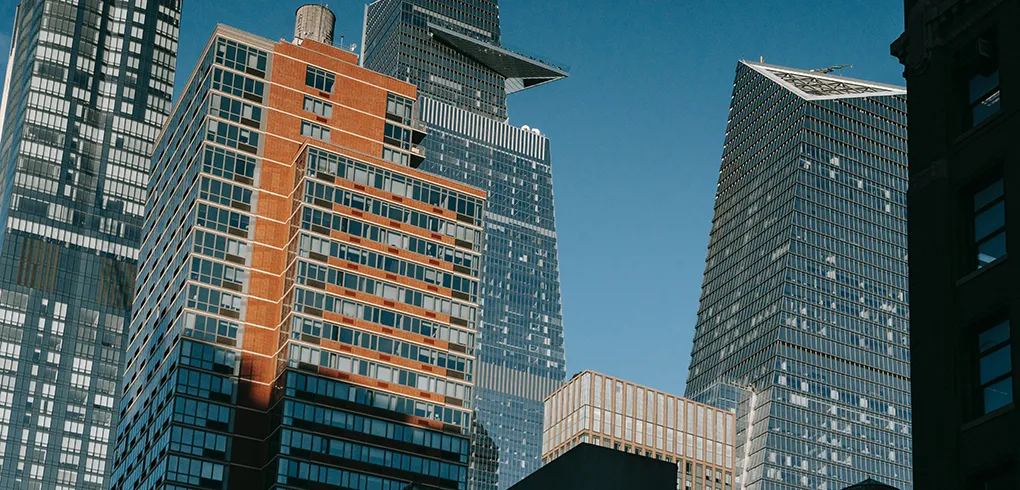
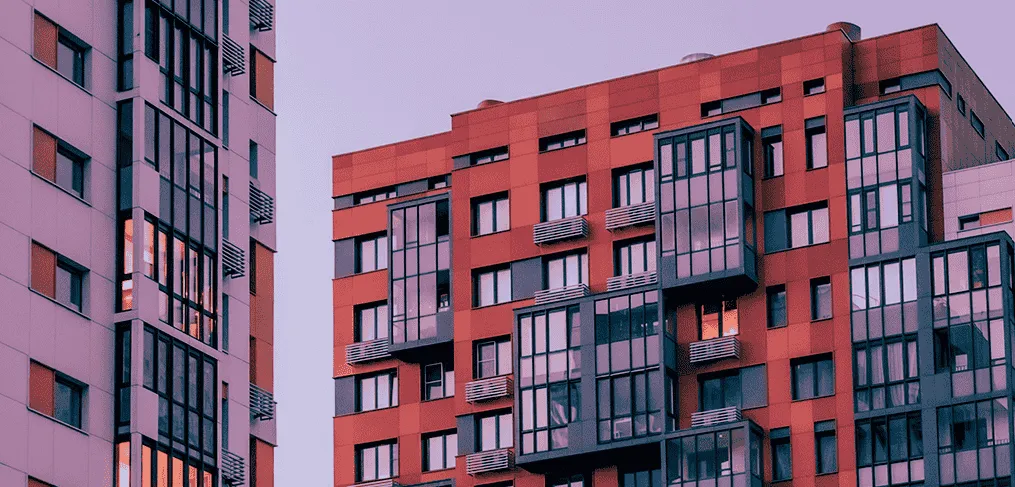
A high-rise flat, also known as a high-rise apartment or tower block, is a residential building characterised by its tall height and multiple floors, typically containing numerous individual apartment units. These buildings are often constructed in urban areas where land is scarce or expensive, and there is a need to accommodate a large number of people within a limited footprint.
There isn’t a precise definition of “high rise” that lenders share. Most tend to think of buildings that are 7 floors or more in height, or buildings that have an elevator. High-rise flats rose to prominence as council buildings – “tower blocks” – in the 1960s and 70s as an affordable means of providing housing for rising numbers of urban dwellers. More recently, more upmarket high-rise apartments are going up across the UK.
Key features of high-rise flats include:
- Height – high-rise flats are tall buildings that rise several stories above ground level. While there isn’t a specific height threshold that defines a high-rise, they typically have more than six or eight floors
- Multiple floors – high-rise flats consist of multiple floors or levels, with each floor containing several individual apartment units. Elevators or lifts are commonly used to access the upper floors
- Residential units – the primary purpose of high-rise flats is to provide residential accommodation. Each floor typically contains multiple apartments of varying sizes and layouts, ranging from studios to larger multi-bedroom units
- Shared amenities – high-rise flats may offer shared amenities and facilities for residents, such as communal areas, gyms, swimming pools, parking facilities, and landscaped gardens. The availability of amenities can vary depending on the building and its management
- Urban location – high-rise flats are often located in urban areas where there is high demand for housing and limited space for horizontal expansion. They may be situated in city centres, residential neighbourhoods, or mixed-use developments
- Architectural design – the architectural design of high-rise flats can vary widely, ranging from modern glass-and-steel towers to more traditional brick or concrete structures. Design considerations may include aesthetics, functionality, structural integrity, and energy efficiency
- Structural considerations – building a high-rise structure requires careful engineering and construction techniques to ensure structural stability, safety, and resilience against factors such as wind, earthquakes, and other environmental hazards